Looping statement defines a set of repetitive statements . These statements are repeated, with same or different parameters for a number of times. While loops are similar to for loops, but have less functionality. A while loop continues executing the while block as long as the condition in the while remains true while loop is an entry controlled looping construct
for loop is easy to implement if you specifically know start and end position of the loop counter. However, things in the real life are not so simple. You may come across situation where you only know when to terminate the loop. For example – reading instructions from user until terminated manually, waiting for client connection until connected or cancelled, reconnecting to the server until connected.
while loop is an entry controlled looping construct. We use while loop to repeat set of statements when number of iterations are not known prior to its execution. It provides flexibility to define loop without initialization and update parts (present in for loop).
Looping statements whose condition is checked prior to the execution of its body is called as Entry controlled loop.
Syntax of while loop
while(condition)
{
// Body of while loop
}In while loop you are free to initialize loop counter variables anywhere in the program before its use. However, best practice is to initialize all important loop variable just before the loop. Likewise, you can keep your loop update part just before the end of loop.
Parts of while loop
Unlike for loop, while does not contain initialization and update part. It contains only two parts - condition and body of loop.
How while loop works?
Simplicity of while loop exists in its working mechanism. while loop works in two steps.
The above two steps are repeated, until loop condition is true
Flowchart of while loop
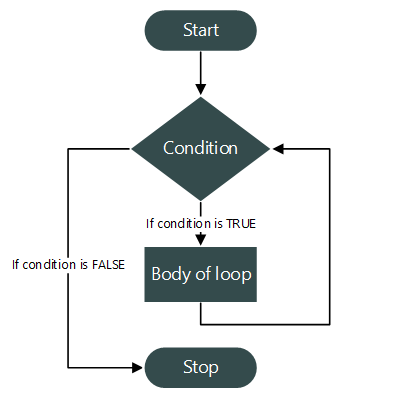
Example to demonstrate while loop
/**
* C program to print natural numbers using while loop
*/
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
/* Loop counter variable declaration and initialization*/
int n = 1;
/* Loop condition */
while(n <= 10)
{
/* Body of loop */
printf("%d ", n);
/* Update loop counter variable */
n++;
}
return 0;
}Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10